The Smart City reinvented by computer vision
Discover how computer vision and AI are redefining smart cities, for smoother, safer and more sustainable infrastructure.
Technology at the service of smart cities
Computer vision combined with artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the Smart City. It optimizes infrastructure management, improves the fluidity of travel and strengthens urban security.



Cutting-edge technologies for urban mobility
Advanced technologies and powerful algorithms are transforming urban mobility management, optimizing travel and sustainability
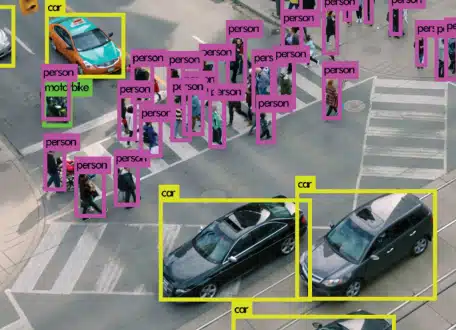
Detection and tracking algorithms
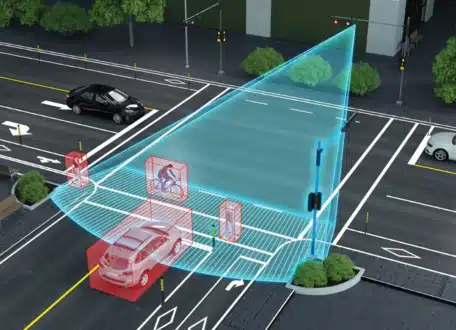
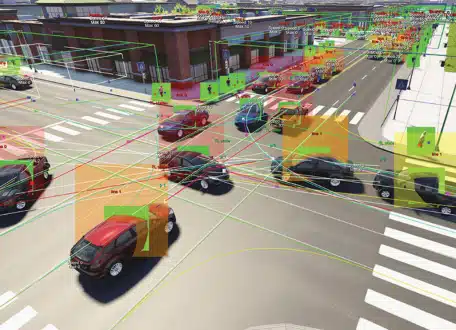
Models like YOLO and Faster R-CNN help identify and localize vehicles, pedestrians and cyclists. To track their trajectories, solutions like DeepSORT and ByteTrack ensure continuous and accurate monitoring

Multispectral vision
Thanks to infrared cameras and LIDAR systems, multispectral vision offers unparalleled perception, whether for nighttime tracking or for accurately measuring distances and volumes in complex environments.

Advanced Neural Networks
CNNs are used to recognize objects and scenes, while RNNs analyze mobility flows across time series, improving prediction of trends and behaviors

Edge computing and multimodal fusion
Smart cameras process data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth consumption. Multimodal fusion integrates this information with sensor data, such as traffic sensors and GPS, for a holistic and coherent view of urban flows.
Challenges and limitations
Challenges to overcome in exploiting the potential of computer vision in the Smart City



Inspiring use cases in the Smart City
These real-world applications illustrate the enormous potential of this technology to make business processes more efficient, secure and personalized.

Singapore
With smart cameras and vision algorithms, Singapore analyzes traffic in real time, reducing congestion and optimizing the punctuality of public transport

Barcelona
Barcelona uses computer vision to analyze pedestrian flows and identify risky behaviors. This approach increases safety and improves the organization of urban spaces

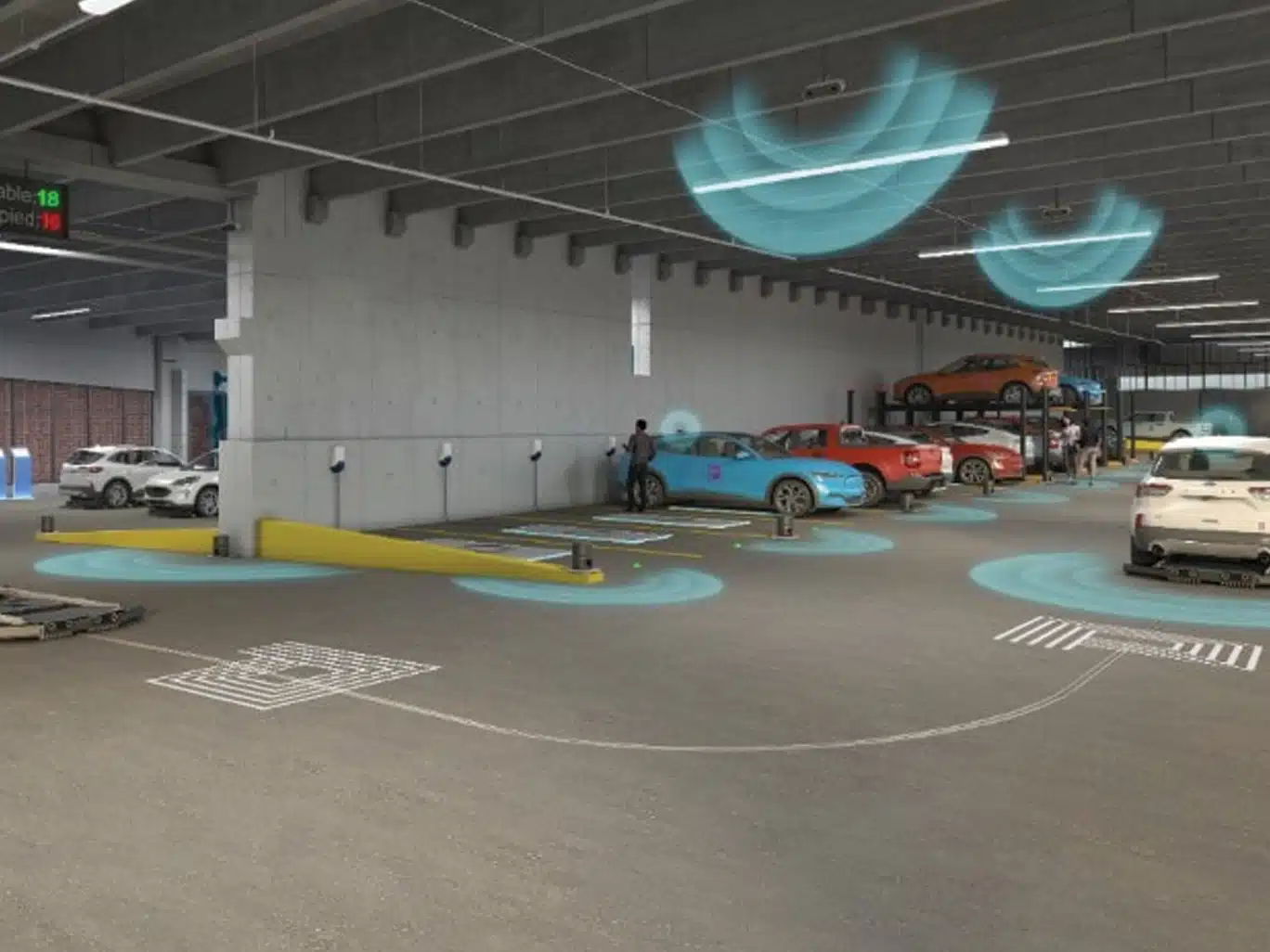
Los Angeles
Vision systems detect vacant spaces and direct drivers, reducing search time and parking-related emissions