Smart Retail in the era of computer vision
Learn how computer vision and AI are transforming customer experiences and optimizing operations
Technology at the service of smart commerce
Computer vision combined with artificial intelligence plays a key role in Smart Retail, improving operational efficiency, personalizing customer experience and preventing losses.



Technologies and algorithms: the pillars of computer vision
Integrating deep learning and edge computing optimizes analysis and secures data in Smart Retail
Deep learning and convolutional networks (CNN)
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are essential for computer vision. They allow image recognition with models such as VGGNet and ResNet, and to perform semantic segmentation using tools such as U-Net and Mask R-CNN.

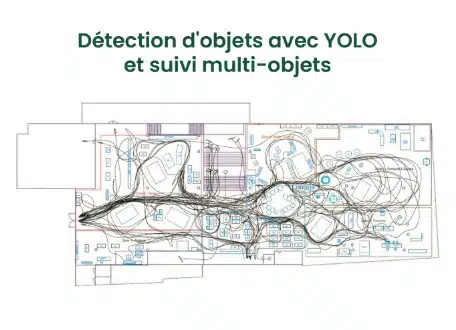
Object recognition and tracking
Algorithms like YOLO and Faster R-CNN are used to identify products and customers. To track their movements, advanced techniques like DeepSORT or ByteTrack are used.
Multimodal vision
Combining data from various sensors (RGB cameras, infrared sensors, LIDAR) increases the accuracy of the models. This multimodal approach optimizes analyses in complex environments
Edge computing processing
Local data processing, via devices, guarantees real-time analyses. This approach reduces latency and strengthens the confidentiality of the information processed.
Challenges and limitations
Challenges to Maximize the Potential of Computer Vision in Retail



Retail innovations: inspiring use cases
These real-world applications illustrate the enormous potential of this technology to make business processes more efficient, secure and personalized.

Using computer vision, Amazon Go delivers a checkout-free shopping experience, eliminating lines and making purchasing faster and more seamless.

Sephora enhances customer experience with virtual try-ons and shopping behavior analysis, adjusting product presentation to meet customer preferences

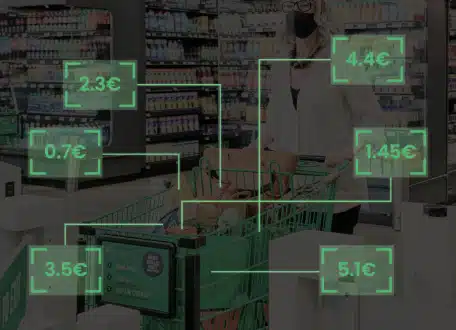
Walmart uses cameras to monitor checkouts and prevent theft, while optimizing inventory management and shelf layout